Why Modular Buildings Are the Future of Construction
The global construction industry is undergoing a massive transformation. With rising material costs, labor shortages, and growing environmental concerns, developers are seeking faster, smarter, and more sustainable building solutions.
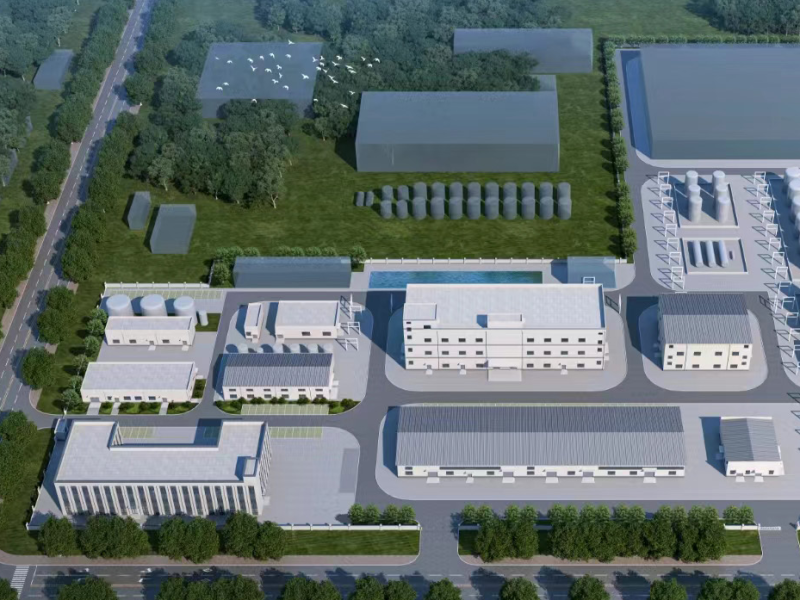
Enter modular construction — a method that assembles buildings from prefabricated modules manufactured off-site and transported for quick installation.
From schools and hospitals to offices, factories, and housing complexes, modular buildings are reshaping how projects are designed, built, and delivered. In this article, we’ll explore why modular buildings represent the future of construction and how they’re revolutionizing global infrastructure.
1. What Is Modular Construction?
Modular construction is a modern building approach where structures are produced in sections (modules) within a controlled factory environment. Each module includes all essential components — from walls and flooring to plumbing and electrical systems — and is assembled on-site to form a complete building.
Unlike traditional construction, which depends heavily on on-site labor and weather conditions, modular methods use industrialized manufacturing processes for greater precision, efficiency, and scalability.
Common types of modular buildings include:
- Residential apartments and worker dormitories
- Office and commercial complexes
- Educational and healthcare facilities
- Hotels and resorts
- Industrial and temporary buildings
2. Why Modular Buildings Are Transforming the Industry
Modular construction offers distinct advantages that traditional methods simply can’t match. These benefits make it the go-to choice for developers, contractors, and governments worldwide.
A. Faster Construction Time
Since modules are produced in a factory while foundation work is completed on-site, the total project duration can be reduced by 40–60%. This dual-track process is ideal for projects with tight deadlines.
B. Cost Efficiency
Factory-based production reduces material waste, labor costs, and rework. Developers can save up to 30% on total construction costs, while achieving consistent quality across all units.
C. Quality Control
All modules are built in a controlled environment, ensuring precision engineering, consistent finishes, and compliance with international standards such as ISO, CE, or ASTM.
D. Reduced Environmental Impact
With minimal on-site waste, optimized material usage, and better energy efficiency, modular buildings are among the most eco-friendly construction methods available.
E. Flexibility and Scalability
Modules can be reconfigured, expanded, or relocated easily. This makes modular buildings ideal for growing businesses, urban expansions, or temporary projects.
3. The Advantages of Factory Prefabrication
The core strength of modular construction lies in off-site prefabrication, which enhances both efficiency and quality.
- Controlled Production: Factories operate under strict supervision, unaffected by weather or labor fluctuations.
- Precision Engineering: Automated cutting, welding, and assembly ensure accuracy within millimeters.
- Integrated MEP Systems: Electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC systems are pre-installed before delivery.
- Reduced Site Disruption: On-site assembly is clean, quiet, and fast — ideal for urban or remote areas.
These efficiencies allow developers to complete complex projects quickly while maintaining global quality standards.
4. Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Potential
Contrary to early perceptions, modular buildings are no longer boxy or basic. Today’s designs are stylish, functional, and customizable.
Architects and engineers can combine modules in endless configurations — stacking, connecting, or offsetting units to achieve unique layouts.
Modern design features include:
- High-quality facades with aluminum, glass, or composite panels
- Open floor plans with removable partitions
- Integrated balconies and rooftop decks
- Advanced insulation and acoustic systems
- Smart technologies for lighting, energy, and access control
The result? Modular buildings that rival — or surpass — traditional structures in both aesthetics and performance.
5. Sustainability: Building Greener with Modular Solutions
Sustainability is one of the strongest drivers of modular construction. Every stage of the process — from manufacturing to installation — is designed to reduce environmental impact.
A. Waste Reduction
Factory-controlled production minimizes offcuts and unused materials. Up to 90% less waste is generated compared to on-site construction.
B. Energy Efficiency
Modules can be designed with insulated panels, solar systems, and natural ventilation, reducing operational energy consumption.
C. Material Reusability
Steel and modular components can be dismantled, relocated, or recycled — supporting a circular economy model.
D. Lower Carbon Footprint
Reduced transportation, energy consumption, and construction waste make modular buildings significantly greener overall.
These eco-friendly advantages make modular construction a key solution for companies pursuing LEED, BREEAM, or other sustainable building certifications.
6. Applications of Modular Buildings Across Industries
Modular buildings are highly adaptable and are used in virtually every industry today:
- Residential: Affordable housing, apartments, and villas
- Commercial: Office buildings, shopping centers, and showrooms
- Education: Schools, training centers, and dormitories
- Healthcare: Clinics, hospitals, and laboratories
- Hospitality: Resorts, modular hotels, and staff accommodations
- Industrial: Factories, control rooms, and warehouses
This versatility allows governments, NGOs, and private investors to deploy infrastructure projects faster and more cost-effectively than ever before.
7. Global Export Opportunities
The export market for modular buildings is expanding rapidly, especially in regions where infrastructure demand outpaces construction capacity.
Exported modular units can be shipped as flat-packed kits or fully assembled containers, ready for plug-and-play installation.
Key export advantages include:
- Compact, standardized packaging for easy transport
- Shorter lead times and predictable delivery
- Simple on-site assembly using bolt connections
- Compatibility with international safety standards
For B2B clients in Africa, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America, modular buildings offer a turnkey solution that minimizes cost and complexity.
8. The Future: Smart, Sustainable, and Scalable Construction
The next generation of modular buildings will integrate smart technologies, renewable energy, and advanced automation.
Emerging trends include:
- Smart IoT monitoring systems for building management
- 3D printing integration for precision customization
- Solar energy and battery storage systems
- Hybrid modular systems combining steel and concrete panels
- Zero-carbon construction through advanced material innovation
As technology evolves, modular buildings will not only accelerate construction but also reshape how we live, work, and build — leading the global shift toward sustainable urbanization.
Conclusion
Modular construction is no longer the future — it’s the present. Combining efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility, modular buildings have proven their ability to deliver high-quality results in less time and at lower cost.
For developers, contractors, and international investors, prefabricated modular solutions offer a smart, scalable way to meet the world’s growing demand for housing and infrastructure.
Whether it’s a school in Africa, an office in Europe, or a factory in Asia, modular buildings are redefining construction for a faster, greener, and more connected world.