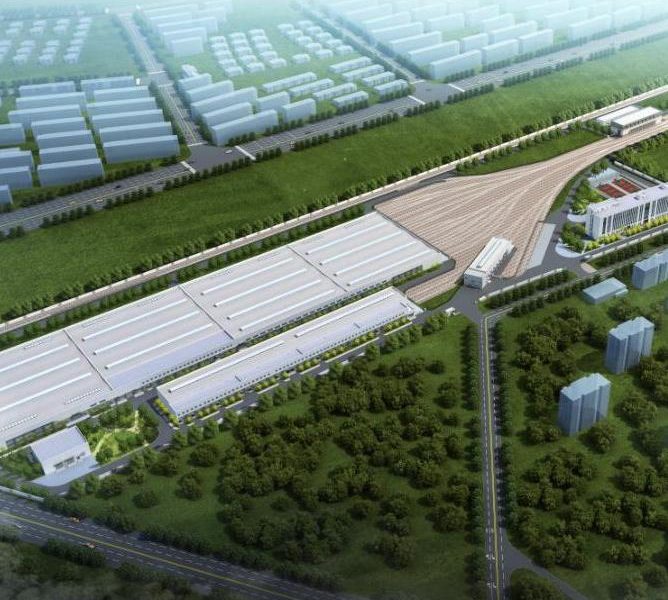
Steel Structure Cold Storage Warehouses: Energy-Efficient and Durable Refrigerated Solutions
In a world where food safety, pharmaceutical integrity, and temperature-controlled logistics are essential, cold storage warehouses play a critical role in maintaining supply chain efficiency.
Modern cold storage facilities require precise temperature control, high insulation performance, and long-term structural reliability.
To meet these demands, steel structure cold storage warehouses have become the preferred choice for industrial developers and logistics companies around the world.
1. The Rising Demand for Cold Storage Facilities
The global cold storage market is expanding rapidly, driven by:
- Growth in the food processing and frozen goods industry
- Expansion of e-commerce and online grocery delivery
- Increased demand for pharmaceutical and vaccine storage
- The need for energy-efficient logistics infrastructure
Traditional concrete cold rooms often face issues with insulation performance, condensation, and slow construction.
Steel structures, by contrast, provide lightweight, fast-built, and thermally efficient solutions designed for modern cold chain logistics.
2. Why Steel Is Ideal for Cold Storage Construction
a. Excellent Thermal Insulation
Steel structures easily integrate with insulated sandwich panels (PU, PIR, or EPS), forming continuous thermal barriers that minimize temperature loss.
b. Fast Construction
Prefabricated steel components can be manufactured off-site and assembled quickly, reducing construction time by 30–50% compared to traditional methods.
c. Hygiene and Clean Design
Steel buildings allow smooth, seamless internal finishes that prevent bacterial growth and make cleaning easier — crucial for food and medical-grade environments.
d. Structural Strength and Durability
Cold storage warehouses often support heavy refrigeration equipment, pallet racks, and loading systems.
Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio ensures superior load-bearing performance and long service life.
e. Energy Efficiency
With high-quality insulated panels and airtight joints, steel cold storage buildings significantly reduce heat transfer and energy consumption.
3. Structural Systems for Cold Storage Warehouses
| Structure Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Portal Frame System | Rigid steel frames with clear spans up to 60m | Cold rooms, food warehouses |
| Multi-Span Steel Frame | Modular design with interior columns | Large-scale logistics centers |
| Steel + Insulated Panels | PU/PIR sandwich wall and roof panels | High insulation performance |
| Steel Mezzanine Floors | For multi-level storage or equipment space | Tiered refrigeration areas |
| Steel Cladding Systems | Corrosion-resistant exterior panels | Long-term durability |
These systems ensure airtightness, load resistance, and temperature stability even under extreme operating conditions.
4. Temperature Zones and Insulation Design
Cold storage warehouses typically consist of multiple temperature zones:
- Ambient zone (10°C to 20°C)
- Chilled zone (0°C to +5°C)
- Frozen zone (-18°C to -25°C)
- Deep freeze zone (-30°C and below)
Steel structures can seamlessly integrate insulated partitions, thermal breaks, and vapor barriers between these zones, ensuring optimal temperature segregation and energy savings.
5. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Energy consumption accounts for up to 60% of total operational costs in cold storage facilities.
Steel buildings improve efficiency through:
- High-performance insulated walls and roofs
- Cool roof coatings and reflective finishes
- Reduced air leakage due to precision joints
- Integration of renewable energy systems (solar, geothermal)
Over a 10-year period, a steel cold storage facility can reduce energy costs by 20–30% compared to conventional concrete structures.
6. Fire Safety and Corrosion Protection
Cold environments and humidity can create corrosion challenges.
Steel cold storage warehouses utilize:
- Galvanized or pre-painted steel sheets
- Protective coatings and anti-condensation layers
- Non-combustible wall and roof materials
- Fire-resistant PU/PIR panels
These measures enhance safety, longevity, and low maintenance requirements in demanding conditions.
7. Construction Process and Speed
A typical steel cold storage project involves:
- Foundation preparation with vapor barrier and insulation layers
- Erection of prefabricated steel frames
- Installation of insulated roof and wall panels
- Air-tight joint sealing and vapor barrier integration
- Installation of refrigeration and HVAC systems
Thanks to prefabrication and modularization, even large-scale projects can be completed in 4–6 months.
8. Hygiene and Maintenance Advantages
Hygiene standards in food and pharmaceutical industries are stringent.
Steel cold storage warehouses meet international requirements such as:
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)
- FDA and ISO 22000 compliance
Smooth, non-porous steel surfaces resist moisture and bacterial buildup, allowing for easy sanitization and long-term cleanliness.
9. Automation and Smart Systems
Modern cold storage facilities increasingly integrate automated material handling systems (AMHS) and IoT-based temperature monitoring.
Steel structures offer the flexibility to support:
- Automated conveyor and racking systems
- Temperature sensors and remote monitoring
- Smart ventilation and defrost systems
- Energy optimization through AI-based control
This combination enhances operational efficiency while reducing labor and energy costs.
10. Case Study: Prefabricated Steel Cold Storage Facility
Project Type: 10,000 m² frozen food warehouse
Temperature Range: -25°C to +5°C
Construction Period: 5 months
Structure Type: Portal frame steel + PU panels
Results:
- Construction time reduced by 45%
- Energy savings of 28% annually
- Achieved LEED Silver certification
- Maintenance costs cut by 35% over five years
This project demonstrates the economic and environmental advantages of adopting steel cold storage structures for modern logistics operations.
11. Long-Term Investment Benefits
| Feature | Steel Structure | Concrete Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Speed | 4–6 months | 8–12 months |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Medium |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | High |
| Hygienic Standard | Excellent | Moderate |
| Expansion Flexibility | Easy | Difficult |
| Recyclability | 100% | Limited |
The long-term savings in energy, time, and maintenance make steel structures a smarter investment for B2B clients.
12. Sustainability and Green Certification
Steel buildings can be designed to achieve:
- Net-zero energy performance
- Solar-ready roof systems
- Low-emission materials
- Recyclable components
With steel’s circular economy advantage, these facilities align with global sustainability goals and ESG reporting standards.
13. Future Trends in Cold Storage Design
Emerging innovations include:
- Hybrid steel-wood structures for lower embodied carbon
- AI-driven temperature management
- Vertical cold storage systems for urban logistics
- Hydrogen-powered refrigeration systems
- Smart insulation with phase-change materials
These trends further enhance efficiency and adaptability for the next generation of cold chain infrastructure.
14. Conclusion
Steel structure cold storage warehouses represent the future of temperature-controlled logistics.
They offer:
✅ Fast and efficient construction
✅ Excellent insulation and hygiene performance
✅ Sustainable and energy-efficient operation
✅ Structural durability and easy expansion
For businesses in food, pharmaceutical, and logistics sectors, investing in prefabricated steel cold storage buildings ensures lower operational costs, higher performance, and long-term value.