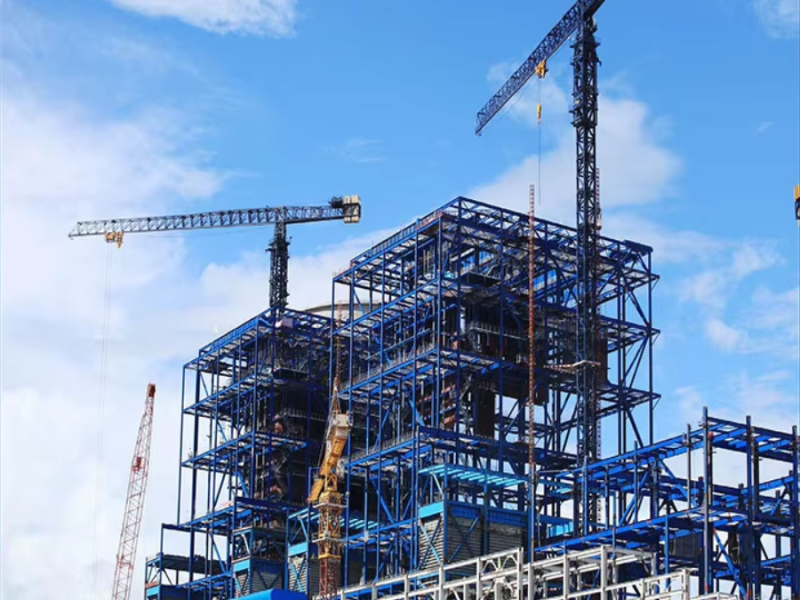
Steel Structure Cold Storage: Energy-Efficient Solutions for the Food Industry
As global demand for fresh and frozen food continues to rise, the cold storage industry has become one of the fastest-growing sectors in modern logistics and agriculture.
From seafood and meat to pharmaceuticals and vaccines, temperature-controlled facilities are vital for maintaining product quality, food safety, and supply chain reliability.
Among all construction types, steel structure cold storage buildings stand out for their energy efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
They are now the preferred choice for businesses seeking sustainable and scalable cold storage solutions.
1. The Importance of Cold Storage in the Modern Food Industry
Cold storage is an essential link between production, processing, and distribution.
It ensures perishable goods maintain freshness and meet global safety standards.
A well-designed cold storage facility must provide:
- Precise temperature control (from +15°C to -40°C)
- High insulation performance
- Hygienic and corrosion-resistant interiors
- Reliable structure for equipment and racking
- Energy-efficient operation
Steel structures meet all these requirements while offering flexibility, speed, and long-term performance unmatched by traditional building materials.
2. Why Steel Is Ideal for Cold Storage Construction
a. Thermal Efficiency
Steel buildings integrate insulated sandwich panels for walls and roofs, minimizing heat transfer and maintaining consistent internal temperatures.
b. Hygienic Design
The smooth surfaces of steel and insulated panels are easy to clean and resistant to bacteria, mold, and pests — critical for food and medical storage.
c. Rapid Construction
Prefabricated steel components are factory-made and quickly assembled on site, significantly reducing downtime and operational delays.
d. Cost and Energy Savings
Due to lightweight design and low maintenance needs, steel cold storages reduce energy and operating costs over their entire lifespan.
3. Structural Design Features of Steel Cold Storage Buildings
A steel cold storage facility is engineered for both strength and insulation performance.
| Component | Function | Steel Design Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Main Frame | Structural support | H-beams, portal frames, galvanized coating |
| Roof | Thermal insulation | PU / PIR sandwich panels with vapor barrier |
| Wall Panels | Temperature control | Food-grade insulated panels |
| Floor System | Load-bearing & insulation | Reinforced base with thermal break |
| Doors | Air seal and hygiene | Automatic insulated cold room doors |
| Refrigeration System | Cooling performance | Integrated with insulated envelope |
Together, these systems create a sealed, thermally stable environment — ensuring constant temperatures even in extreme climates.
4. Temperature Zones and Applications
Steel structure cold storages are adaptable for different temperature ranges and product types:
| Temperature Range | Application |
|---|---|
| +10°C to +15°C | Fresh fruits, vegetables, dairy |
| 0°C to +5°C | Beverages, pharmaceuticals |
| -10°C to -20°C | Frozen meat, seafood, bakery products |
| -25°C to -40°C | Deep-freeze and long-term preservation |
This versatility allows businesses to customize cold storage layouts for multi-zone or single-temperature operations.
5. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy consumption is one of the biggest expenses in cold storage operations.
Steel structures improve efficiency through:
- High-performance insulation panels (PU/PIR/EPS)
- Tight sealing to prevent air leakage
- Cool roofing to reflect sunlight
- Integration with solar energy systems
- LED and smart ventilation systems
With proper design, a steel cold storage can reduce energy costs by up to 35% compared to conventional buildings.
6. Durability and Corrosion Protection
Cold environments can be harsh — with high humidity and condensation risks.
Steel structures overcome these challenges with galvanized or epoxy-coated surfaces, ensuring corrosion resistance even in constant cold conditions.
In addition, the non-porous finish of steel prevents the growth of bacteria, maintaining hygienic conditions throughout the storage facility.
7. Rapid Construction and Scalability
Time is critical when dealing with perishable goods.
Steel cold storage systems are prefabricated, meaning:
- Components are pre-cut and pre-drilled
- Minimal on-site welding
- Faster assembly with bolted connections
This allows operators to launch new facilities within months, not years.
Moreover, modular steel structures can easily be expanded as storage demand grows — adding new cold rooms, loading docks, or processing zones without major reconstruction.
8. Fire Safety and Compliance
Steel cold storage facilities meet international safety standards, offering:
- Non-combustible materials
- Fire-rated insulated panels
- Advanced smoke detection systems
- Automatic fire suppression and ventilation controls
Compliance with HACCP, ISO, and FDA standards ensures suitability for both food and pharmaceutical industries.
9. Comparison: Steel vs. Concrete Cold Storage
| Feature | Steel Structure | Concrete Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | 3–5 months | 8–12 months |
| Insulation Integration | Built-in with panels | External layer required |
| Thermal Efficiency | Excellent | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Minimal | High |
| Expansion | Easy | Difficult |
| Energy Consumption | 20–35% lower | Higher |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher ROI | Higher upfront cost |
The numbers are clear — steel structure cold storages offer superior performance, flexibility, and energy efficiency across all key metrics.
10. Common Cold Storage Applications
Steel structure cold rooms are widely used in:
- Food processing and packaging plants
- Frozen seafood and meat storage
- Fruit and vegetable preservation
- Dairy and beverage industries
- Pharmaceutical cold chain logistics
- E-commerce grocery fulfillment centers
Each project can be tailored to specific temperature and layout requirements, making steel the most versatile option in cold chain infrastructure.
11. Case Example: Frozen Seafood Warehouse
A 5,000 m² steel cold storage built near a coastal port:
- Temperature range: -25°C to -35°C
- Insulation: 100 mm PU sandwich panels
- Structure: Hot-dip galvanized steel frame
- Construction period: 4 months
- Energy savings: 30% vs concrete
- Expansion: +2,000 m² added later without operational interruption
This case highlights the scalability and efficiency that steel brings to modern cold storage projects.
12. Long-Term ROI and Operational Benefits
Although initial investment varies by design and capacity, the total cost of ownership for steel cold storage is significantly lower due to:
- Reduced energy bills
- Minimal maintenance
- Longer lifespan
- Higher resale or relocation value
Over 20 years, operators can save up to 25–30% in overall operational costs compared to concrete structures.
13. Global Cold Chain Growth
According to market data, the global cold storage market is projected to exceed USD 350 billion by 2030, driven by food exports, pharmaceuticals, and online grocery demand.
Regions such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are witnessing rapid growth in prefabricated steel cold storage facilities, thanks to their:
- Short construction timelines
- Cost efficiency
- Long-term sustainability
Steel is not just a material — it’s the foundation of the modern cold chain ecosystem.
14. Conclusion
Steel structure cold storage buildings combine engineering strength, energy performance, and hygienic design — making them the best solution for temperature-controlled industries.
From frozen food logistics to pharmaceutical storage, steel offers:
✅ Faster construction
✅ Superior insulation
✅ Low maintenance
✅ Sustainable energy savings
✅ Easy expansion for growing businesses
For enterprises aiming to build reliable and future-ready cold chain facilities, steel is the ultimate choice for efficiency and performance.